How Does Ozone Work?
The third oxygen atom of ozone is extremely reactive because it is unstable. This atom readily attaches itself to other odor molecules. When contaminants such as odors, bacteria or viruses make contact with ozone, their chemical structure is changed to less odorous compounds. Ozone not only destroys bacteria cells, but it does it without leaving a residual affect.
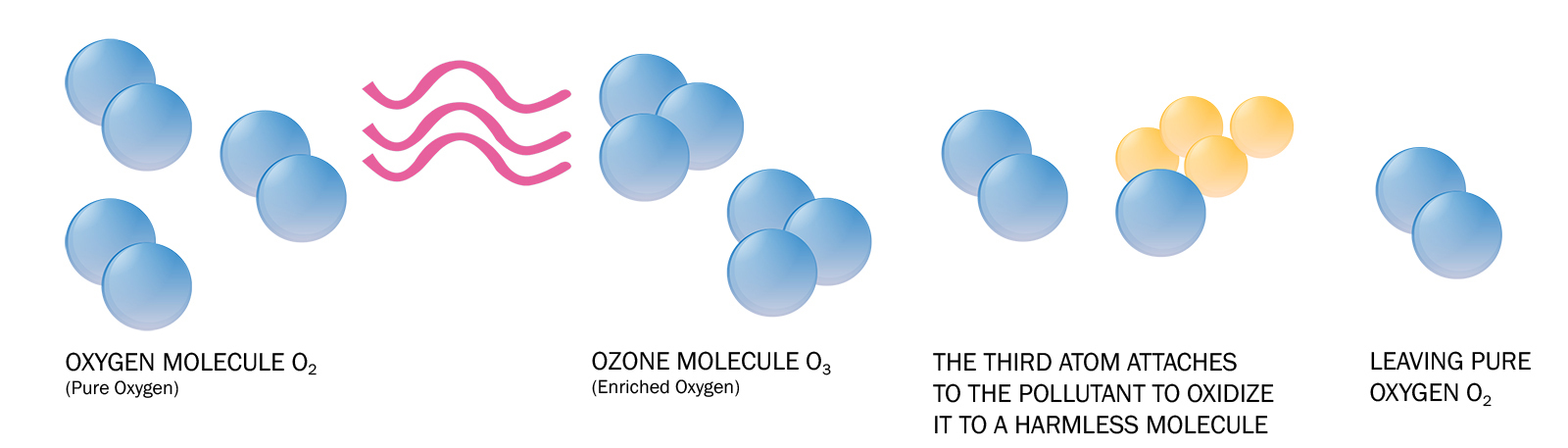
Ozone not only destroys bacteria cells, but it does it without leaving a residual effect. Ozone does this via Oxidative Burst; a process even our own bodies use to protect itself! See the effects ozone has on bacteria in the 6 steps below.

Picture One: This is a healthy bacillus bacterial cell.
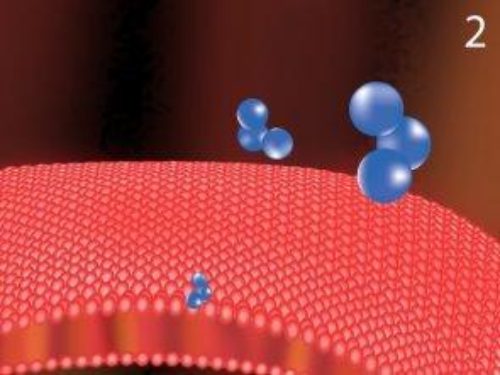 Picture Two: Ozone comes into contact with the cell wall. The cell wall is vital to the bacteria because it ensures the organism can maintain its shape.
Picture Two: Ozone comes into contact with the cell wall. The cell wall is vital to the bacteria because it ensures the organism can maintain its shape.
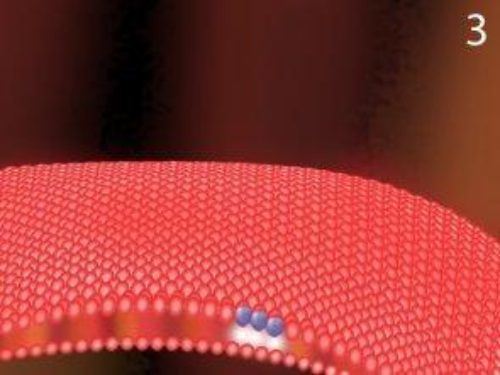 Picture Three: As ozone molecules make contact with the cell wall, an oxidative burst occurs creating a tiny hole in the cell wall.
Picture Three: As ozone molecules make contact with the cell wall, an oxidative burst occurs creating a tiny hole in the cell wall.
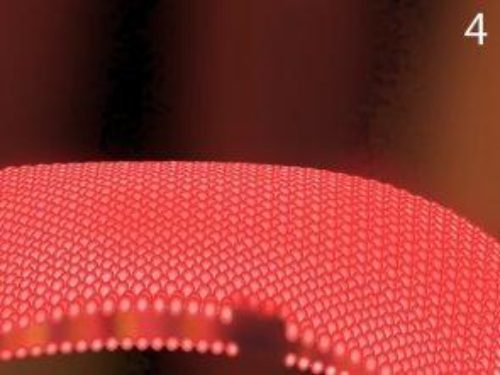 Picture Four: A newly created hole in the cell wall has injured the bacterium.
Picture Four: A newly created hole in the cell wall has injured the bacterium.
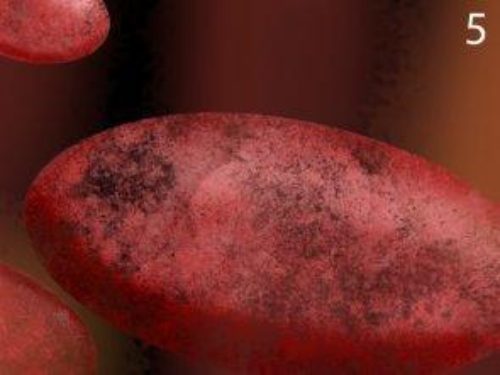 Picture Five: The bacterium begins to lose its shape while ozone
molecules continue to create holes in the cell wall.
Picture Five: The bacterium begins to lose its shape while ozone
molecules continue to create holes in the cell wall.
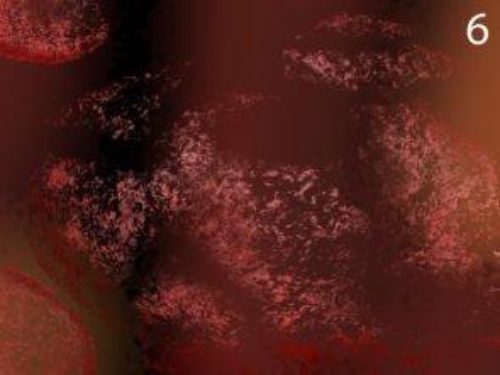 Picture Six: After thousands of ozone collisions over only a few seconds, the bacterial wall can no longer maintain its shape and the cell dies.
Picture Six: After thousands of ozone collisions over only a few seconds, the bacterial wall can no longer maintain its shape and the cell dies.

