Ozone and Milling
The use of ozone in milling applications has grown substantially since 1997, when ozone was first allowed in food processing applications. There are many areas of use for ozone in the milling industries and as research continues new uses will surely follow.
Overview of Ozone Use in Milling Applications
- Ozone is an oxidant used for antimicrobial and pathogen control in many food processing applications
- Ozone was first allowed in food processing in 1997 with limited application
- Ozone was given GRAS approval by both the FDA and the USDA in 2001
- Ozone use in milling has been growing with ongoing research in many areas
Applications of Ozone in Milling Applications
There are many uses for ozone in the milling industry. While some research is on-going, below is a list of industrial applications where ozone has been used with success.- There are many uses for ozone in the milling industry. While some research is on-going, below is a list of industrial applications where ozone has been used with success.
- Aqueous ozone is used in the grain temper process to inactivate mold and bacteria at the first point of the milling process
- Ozone gas is used for surface sanitation of enclosed equipment
- Ozone gas is used on conveyors and transport equipment in process as an antimicrobial intervention point between process steps
Ozone Use in the Temper Process
- The temper process adds water to the grain
- Many grains are tempered to increase the moisture content of the grain prior to milling
- Ozone can be dissolved into the water that is soaked into the grain
- Most pathogens are found on the exterior of the grain
- Fewer pathogens are found within the grain
- Ozone use in the temper process lowers all pathogen levels in the beginning of the milling process
Details of Ozone Use in the Temper Process
Water used in tempering process passes through an ozone injection system to provide aqueous ozone at very high dissolved ozone levels. A minimum of 10 ppm of dissolved ozone is used to ensure residual aqueous ozone can soak completely through the outer later of the grain. Ozone half life in water is 20 minutes in 20-deg C water. After 60 minutes ozone level in water may still be above 2.0 ppm. Aqueous ozone at 2.0 ppm is sufficient for antimicrobial intervention. Aqueous ozone at 2.0 ppm will achieve a four (4) log reduction of bacteria in one (1) second of contact time.
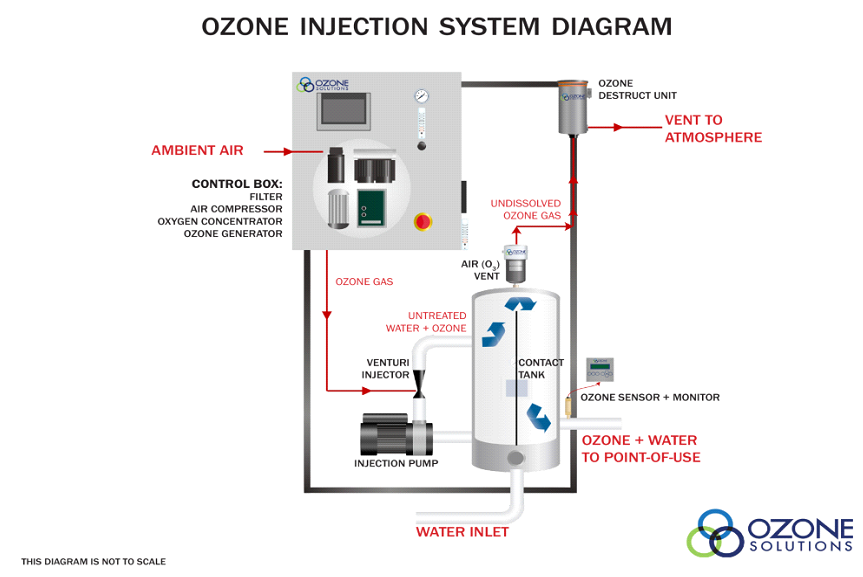
Ozone Gas Use in Milling (ozone gas used on milled grain products in process)
- Sealed mixers can be used to mix ozone gas and milled grains (flour, bran, etc.). Mixers commonly used to inject chlorine gas or other chemicals could be used to apply ozone gas to the milled grain. Contact times greater than 30 seconds at ozone levels greater than 20 ppm will achieve excellent reductions in pathogens.
- Ozone can be introduced into pneumatic or mechanical conveyors to disinfect grain in process. Conveyers that are used to transport milled grains from one location to another can be used to apply ozone gas to the grain. This is an efficient and convenient method of applying ozone gas to the grain.
- Equipment can be sanitized by ozone gas disinfection. Milling equipment can be sealed and exposed to high levels of ozone gas. Ozone gas at effective levels for pathogen reduction can be used in these applications to safely reduce pathogens without the use of chemicals or residuals.
- Ozone gas requires more contact time and higher levels than aqueous ozone.
Practical Information
- The use of ozone in milling has shown increased reduction of bacteria, yeast and mold reduction over time. Due to cross contamination, residual mold spores and residual pathogens, mold and bacteria counts in the final product are not dramatically improved immediately. However, over time the mold and bacteria counts are lowered with the use of ozone in process.
- Customers have commented on reduction and complete elimination of mold growth in sifters and other equipment throughout the milling process.
- Shelf life of some milled products has increased dramatically due to lower bacteria and mold counts.
Research
IOA User Success Report -- Harvest States Amber Milling, Huron, OH- Ozone was used in temper process to replace chlorine.
- APC bacteria reduction of 75-80% using ozone, compared to chlorine.
- After months of operation further reduction of bacteria (up to 95%) was achieved.
Influence of Tempering with Ozonated Water on the Selected Properties of Wheat Flour -- Department of Food Engineering, University of Gaziantep -- Senol Ibanoglu (Oct 14, 2000.)
- Aqueous ozone at 1.5 and 11.5 ppm were tested.
- No physical properties or baking quality changes were found.
- Statistically significant reduction in total bacteria and yeast/mold population was found at both ozone levels.
A Comparison Between Chlorinated Water and Ozonated Water as an Antimicrobial Treatment During Tempering of Wheat -- ASABE Meeting Presentation
- Ozonated water did not have any effect on the color and germination capacity of wheat grains.
- Ozonated water significantly lowered the yeast/mold counts in durum and hard red spring wheat.
