What is Ozone & How Does Ozone Work?
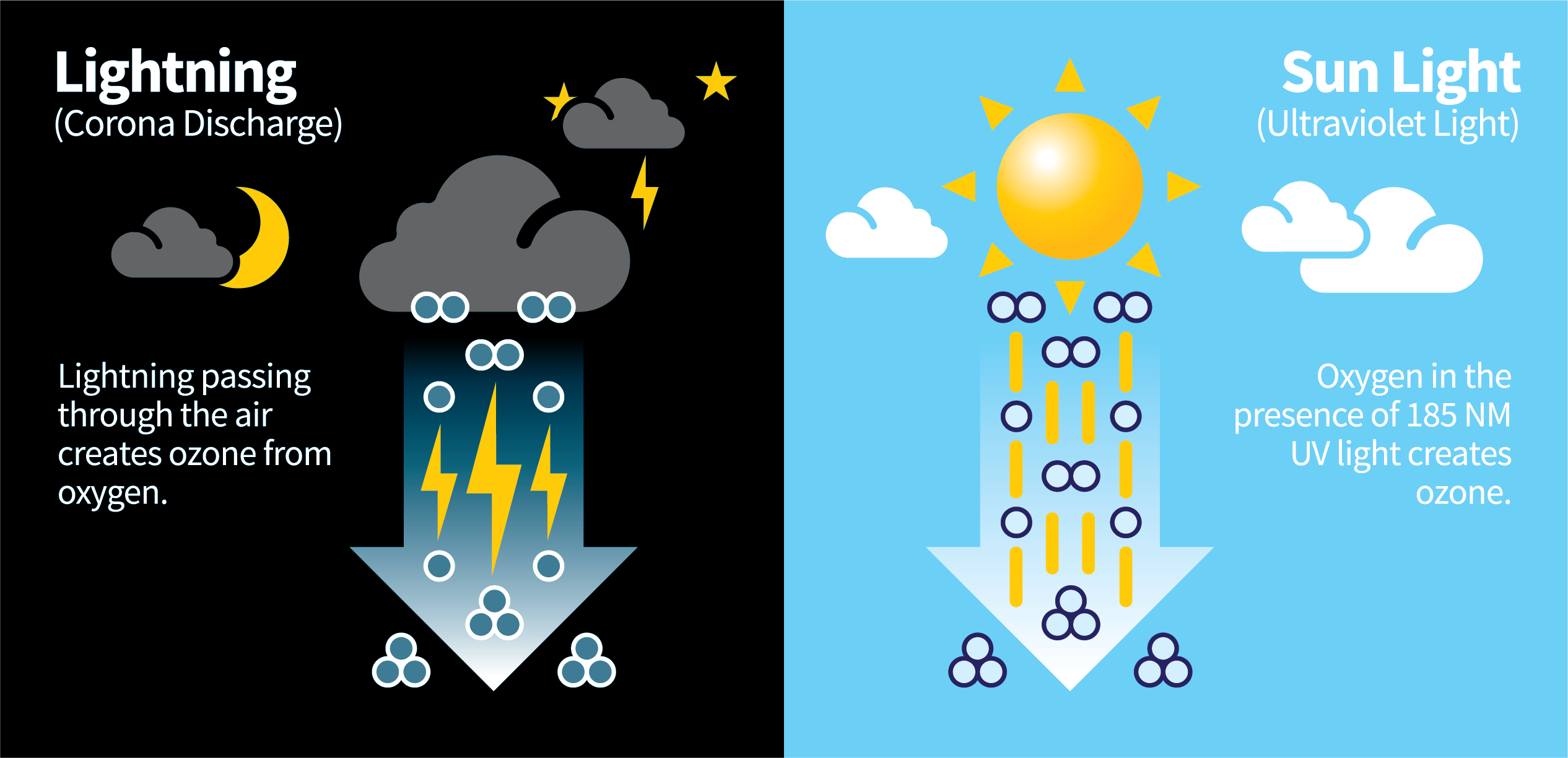
When someone asks, “What is ozone?”, your first thought is probably of the earth’s protective ozone layer that shields us from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays. That’s the ozone we are most familiar with, but ozone isn’t found only in the atmosphere, it occurs quite readily in nature and is formed from oxygen molecules. Two atoms of oxygen form the basic oxygen molecule that is essential to life. Ozone is a molecule composed of three atoms of oxygen. Ozone is created when the two oxygen atoms are broken apart through an electrical charge into single atoms, then reattached to another (two-atom) oxygen molecule.
In nature, this process is created through one of two methods: The first is Corona Discharge, most often as a result of lightning strikes that occur during thunderstorms. In fact, many people probably recognize the smell of ozone. The fresh, clean, spring rain aroma that we notice after a storm is most often a result from nature's creation of ozone. The second method of ozone creation is Ultraviolet Light. Through this method, oxygen in the presence of the sun’s UV light can be broken down and reformed into ozone.
Why use ozone?
Ozone (O3), sometimes marketed as "activated oxygen," is naturally unstable because of the third oxygen atom. That means ozone is extremely reactive. One atom can easily split from the other two atoms of the oxygen molecule and attach itself to other substances or organisms.
This instability makes ozone one of the most powerful sterilizers in the world. Once ozone is produced by an ozone generator, it can attach itself to a pollutant - often long-chain carbon (organic) molecules - and break down their chemical structure into less complex (and typically less harmful) molecules through oxidation. Oxidation enables ozone to destroy airborne and waterborne bacteria, viruses, molds, and odors. Ozone is most widely known for its odor-eliminating abilities, but it is also a powerful water treatment option.
When compared with other disinfection options such as chlorine, ozone offers numerous advantages. First, ozone can eliminate most pollutants far quicker than chlorine. Second, while chlorine has a lower initial investment, the monthly cost for chlorine are much higher than most ozone applications. Finally, ozone not only destroys bacteria cells, but it does so without leaving a chemical residue. The byproduct of ozone is oxygen, making ozone the environmentally friendly option.

What are ozone generators?
So how do we capture ozone from the environment? Because ozone reverts to oxygen over a short period, ozone cannot be captured naturally or pre-packaged and delivered in tanks. Instead, ozone must be produced on-site by an ozone generator. Ozone generators, often referred to as ozone machines, produce ozone by adding energy to oxygen molecules, which causes the oxygen atoms to separate and recombine with other O2 molecules. Just like in nature, they do this in one of two ways:
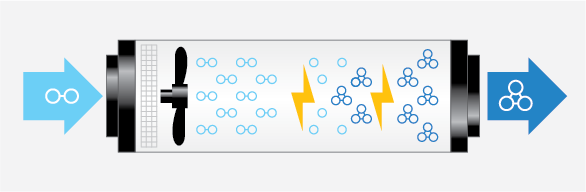
- Corona discharge: These machines produce ozone through a method equivalent to lightning, with electrical energy or "miniature lightning bolts" splitting the oxygen molecules to form ozone. This method is commonly used in high volume ozone applications.
- Ultraviolet radiation: This process of ozone generation is comparable to how the sun’s ultraviolet radiation splits O2 molecules to form individual oxygen atoms. According to InterNACHI, this process is considered to be less efficient than corona discharge.
Below is a diagram visualizing how a corona discharge ozone generator operates.
There are two important factors to consider when choosing an ozone generator. First is determining the correct size ozone generator, and second is making sure you can accurately monitor and control the ozone levels. The specifics of your application will determine correct system sizing. Often that can be accomplished with our existing models. If you require a tailored approach, we can help you design the perfect system for your needs.
However, when you produce ozone on an industrial scale, ensuring the correct level of ozone is necessary for safety and success. Choosing the right ozone monitor is imperative. Ozone Solutions is here with dedicated monitor experts to ensure you make the right choice.
Is ozone harmful?
Ozone is attractive as an alternative to chemical processes like chlorine, which present significant safety challenges, but monitoring ozone levels is necessary to ensure a safer process. Low-level exposure to ozone has not been shown to present long-term health problems. In fact, Ozone has been given GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) approval by the USDA and the FDA for direct contact with food products, including all meat and poultry products meant for human consumption.
However, high levels of ozone in the air we breathe can be harmful. Breathing high levels of ozone can trigger a variety of health issues, including chest pain, coughing, throat irritation, and airway inflammation. Long-term exposure can cause damage to lung tissue. Therefore, ozone levels should be monitored closely when using ozone in an occupied space. In any ozone implementation where people are present, it is important to make sure safety protocols are followed, and there is proper ventilation and/or ozone destruction.
There are several governmental regulations regarding the use of ozone in the workplace, including:
- OSHA requires that ozone levels around workers remain below 0.1 ppm
- OSHA requires that an ambient ozone monitor be in use for generators that produce more than 5 g/hr.
- The USDA and FDA regulate how ozone may be used in food.
You can learn more about the health effects of ozone from the EPA.
If you want to learn more about how ozone works, or if you have specific questions about an ozone system for your company, reach out and ask us.
